Xrdp is an open source version of Microsoft's Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) which allows you to access a remote computer graphically. It works as a remote access solution by linking graphics from an X Windows system to the RDP client, and passing control from the RDP client back to X Windows.
Using RDP, you can log in remotely and set up a desktop session just as you would on your local computer. Linux, Windows, MacOS and Android all support RDP.
In this tutorial, we will use Debian 11 to show you how to install an XRDP server and connect to a VM running an XRDP server using standard Windows tools.
Debian 11 is not included in our templates, but it is easy to install by uploading the installation image to your personal VCD directory. We have described it here.
During the installation of Debian 11, you will be given the option to install a graphical user interface:
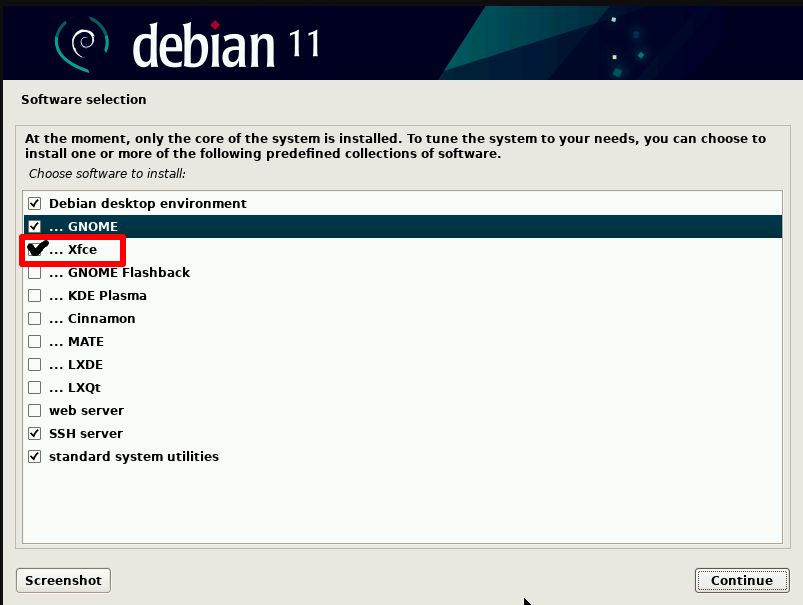
We recommend that you choose Xfce as it is a light and fast desktop environment, making it "ideal" for use on a remote server.
Next, once you have access to your VM via the web console from the VCD, you need to install XRDP, which can be done in a terminal with the following command
sudo apt install xrdp -y
The installation should take less than a minute, once done check the status of the installed service:
sudo systemctl status xrdp
You should see something like this:
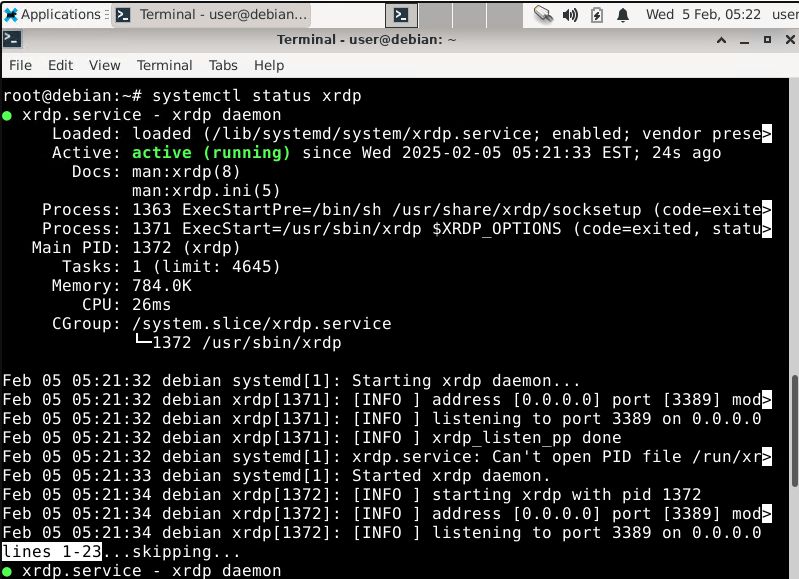
To organise remote access in the cloud, all we need to do is forward the RDP port (3389) to the VM.
In this article we described how to do it.
Now you can connect to Debian 11 the same way you connect to windows, via RDP:
Press Win+R and in the dialog window type mstsc.exe and click OK.
Enter your external IP address in the appeared window (if you are wondering how to find out your IP – watch this video)
Click Connect and in the opened window, enter the username/password of the user you would like to log in with:
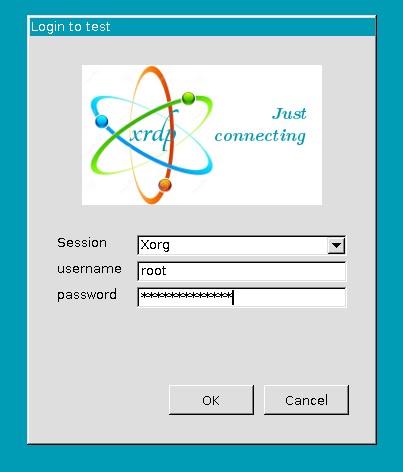
Click OK. You are now connected to your VM using XRDP.
