Prerequisites
0. Install PHP
Ensure PHP is installed and available in your system path.
- Install Composer
Navigate to your project directory and install Composer composer.phar
php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
php composer-setup.php
php -r "unlink('composer-setup.php');"2. Install the AWS SDK for PHP
Run the following command in your project directory:
php composer.phar require aws/aws-sdk-phpConfigure Your Credentials
3. Obtain Your Security Keys
-
Log in to the Cloud4U administration panel:
https://cmc.objstor.cloud4u.com:8443
2. Use credentials provided by Cloud4U support or your S3 administrator.
3. Navigate to Security Credentials and note your Access Key ID and Secret Key.
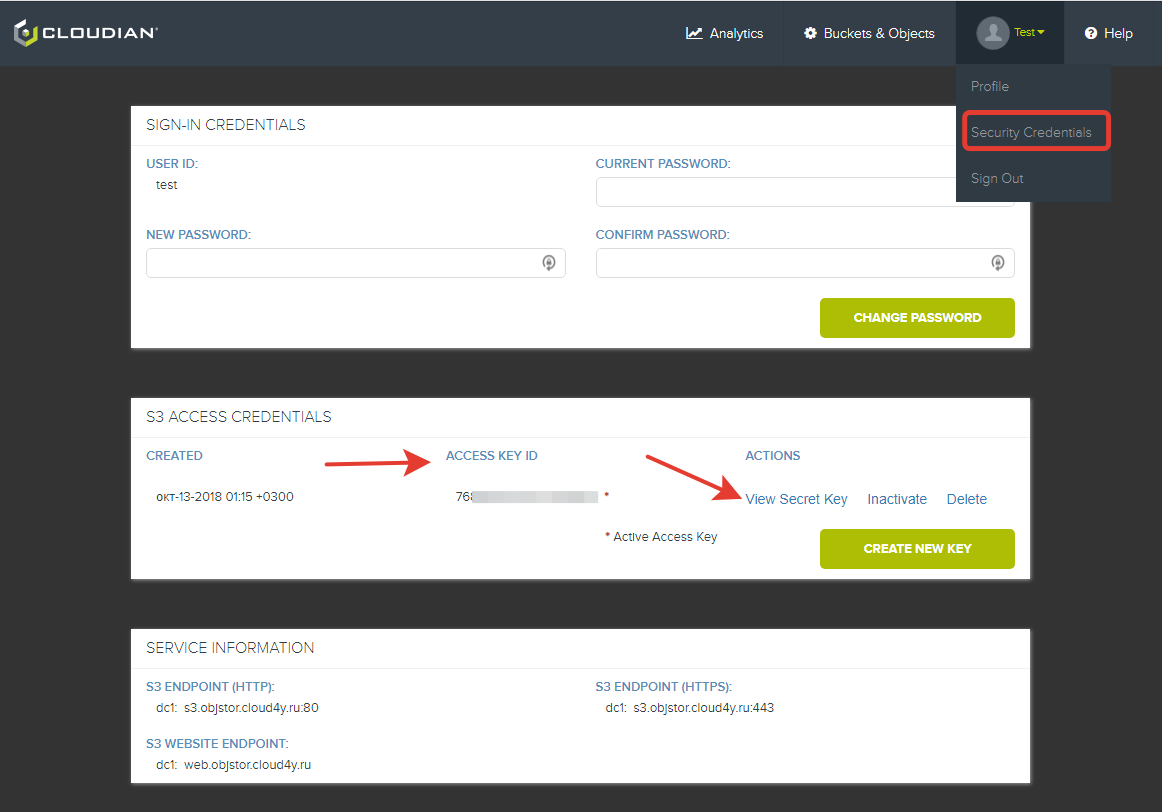
Initialize the S3 Client
4. Create a PHP File and Configure the S3 Client
<?php require 'vendor/autoload.php'; use Aws\S3\S3Client; use Aws\S3\ObjectUploader; use Aws\S3\MultipartUploader; use Aws\Exception\MultipartUploadException; #Create an s3 instance $s3 = new S3Client([ 'version' => 'latest', 'region' => 'msk', 'use_path_style_endpoint' => true, 'credentials' => [ 'key' => 'KEY', 'secret' => 'SECRET', ], 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.objstor.cloud4u.com' ]);
Basic S3 Operations
5. Create a Bucket
<?php #Create bucket via api $s3->createBucket(['Bucket' => 'my-new-bucket']); #Check if the new bucket has appeared in the general list $listBuckets = $s3->listBuckets(); echo '<pre>'; var_export($listBuckets->toArray()['Buckets']); echo '</pre>';

You can also verify bucket creation in the Cloud4U administration panel.
6. Upload and Retrieve an Object
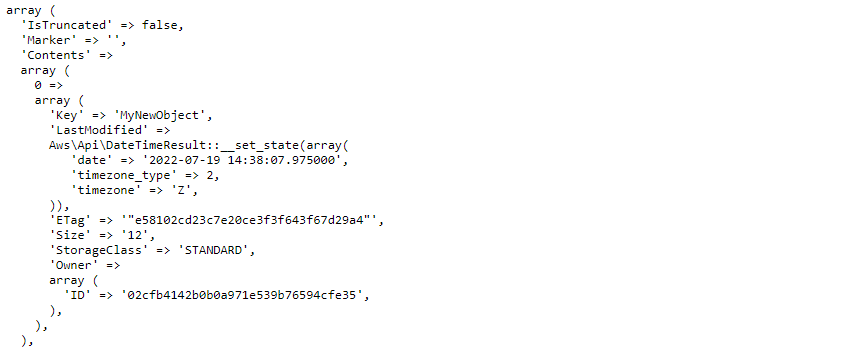
<?php #Load the object from the line $s3->putObject([ 'Bucket' => 'my-new-bucket', 'Key' => 'MyNewObjectForDelete', 'Body' => 'MyObjectBody1', ]); #Get an object $result = $s3->getObject([ 'Bucket' => 'my-new-bucket', 'Key' => 'MyNewObjectForDelete' ]); echo '<pre>'; var_export($result->toArray()); echo '</pre>';
7. Delete an Object
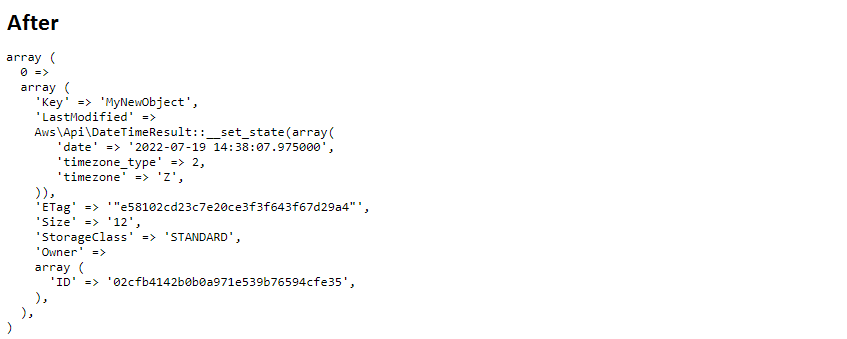
<?php echo '<h2>Before</h2>'; #Get a list of objects $result = $s3->listObjects([ 'Bucket' => 'my-new-bucket' ]); echo '<pre>'; var_export($result->toArray()['Contents']); echo '</pre>'; #Delete an object $s3->deleteObject([ 'Bucket' => 'my-new-bucket', 'Key' => 'MyNewObjectForDelete' ]); echo '<h2>After</h2>'; #Get a list of objects $result = $s3->listObjects([ 'Bucket' => 'my-new-bucket' ]); echo '<pre>'; var_export($result->toArray()['Contents']); echo '</pre>';
out of two objects, there is one left

Advanced Upload Methods
8. Multipart Upload (For files 5MB to 5TB)
<?php #Using stream instead of file path $source = './bff-107mb.zip'; $uploader = new MultipartUploader($s3, $source, [ 'bucket' => $bucketName, 'key' => 'my-file.zip', ]); #Error recovery do { try { $result = $uploader->upload(); } catch (MultipartUploadException $e) { $uploader = new MultipartUploader($s3, $source, [ 'state' => $e->getState(), ]); } } while (!isset($result)); # Abort a download if it fails try { $result = $uploader->upload(); } catch (MultipartUploadException $e) { #State includes "Bucket", "Key", "UploadId" $params = $e->getState()->getId(); $result = $s3->abortMultipartUpload($params); } echo '<pre>'; var_export($result->toArray()); echo '</pre>'; }
9. Smart Upload with ObjectUploader
Use ObjectUploader when unsure whether to use putObject or MultipartUploader. It automatically selects the appropriate method based on file size.
<?php $source = fopen('./bff-107mb.zip', 'rb'); $uploader = new ObjectUploader( $s3, 'my-new-bucket', 'file.zip', $source ); do { try { $result = $uploader->upload(); if ($result["@metadata"]["statusCode"] == '200') { print('<p>File successfully uploaded to ' . $result["ObjectURL"] . '.</p>'); } print($result); } catch (MultipartUploadException $e) { rewind($source); $uploader = new MultipartUploader($s3, $source, [ 'state' => $e->getState(), ]); } } while (!isset($result)); fclose($source);
10. Verify Upload Success
Check uploaded files in the Cloud4U administration panel or using the listObjects method.
For detailed documentation and additional examples, visit the AWS SDK for PHP GitHub repository.
