Key Components
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| ![VDC] | Virtual Datacenter Boundary |
| ![VM] | Virtual Machine (or VM group) |
| ![Cloud Network] | Virtual Switch (Created in Cloud Director) |
| ![Edge] | Edge Gateway (Router/Firewall/NAT) |
Addressing Standards:
-
Private: 192.168.0.0/16 (RFC1918)
-
Public: 192.0.2.0/24, 198.51.100.0/24 (RFC5737)
Option 1: Basic NAT Configuration
Topology:
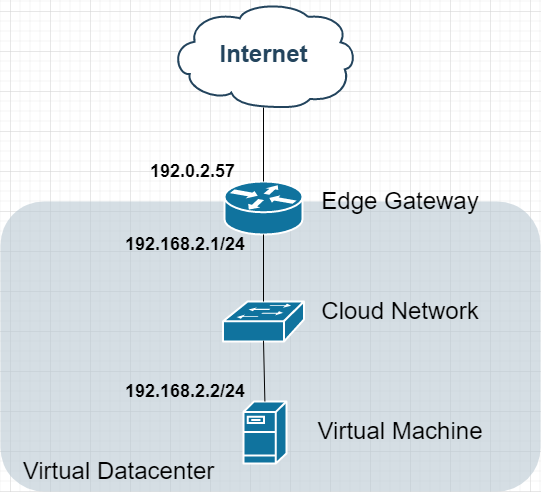
Characteristics:
-
1 public IP on Edge Gateway
-
VMs use private IPs
-
Outbound internet via Source NAT
-
Inbound access via Destination NAT rules
Use Case: Default test environment configuration
Option 2: Multi-IP Edge Gateway
Topology:
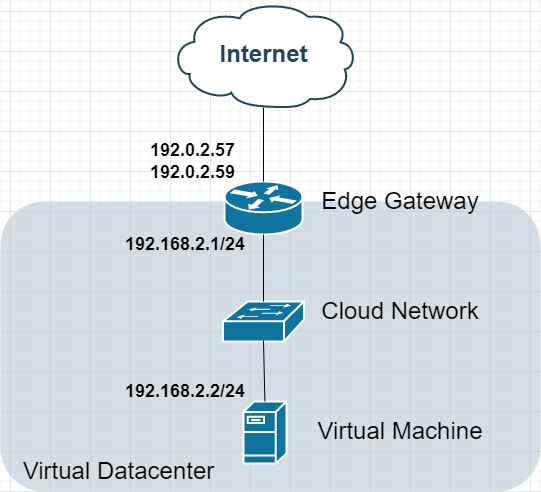
Advantages:
-
Multiple public IPs for different NAT services
-
Improved service isolation
-
Flexible port forwarding rules
Option 3: Multi-Network Segmentation
Topology:
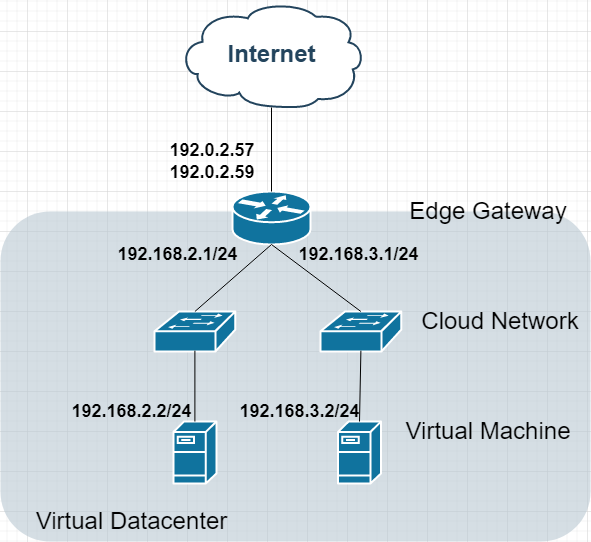
Security Benefits:
-
Isolated network segments
-
Granular firewall policies
-
Separate NAT rules per network
Option 4: Multi-Edge Gateway Deployment
Topology:
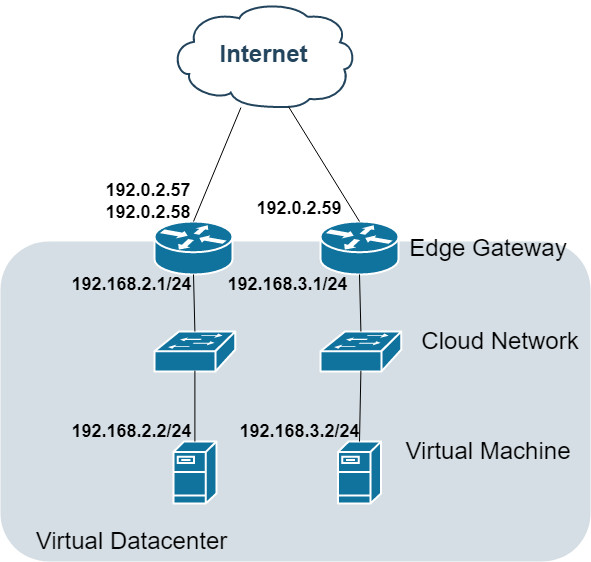
Enterprise Features:
-
Separate security domains
-
Avoids hairpin NAT scenarios
-
Cross-network routing via dedicated links
Option 5: Public IP Assignment
Topology:
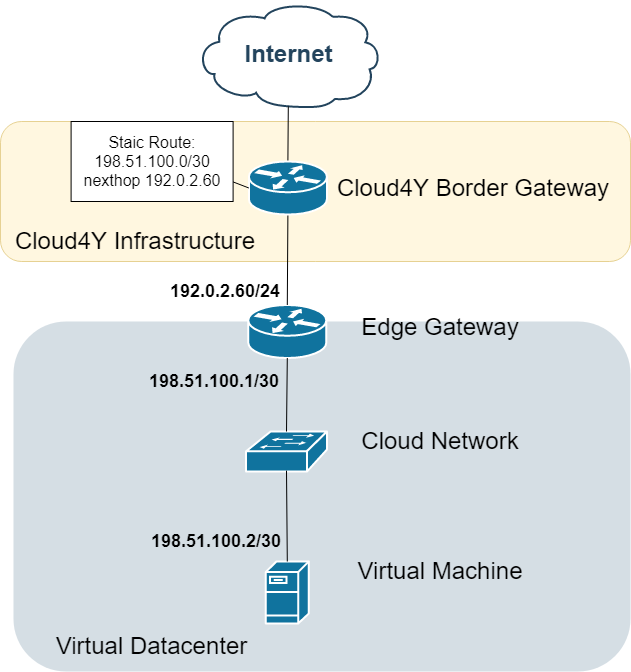
Implementation Notes:
-
Available subnet sizes: /30 to /28
-
Typical /30 allocation:
-
.0: Network address
-
.1: Edge GW (internal)
-
.2: Assignable to VM
-
.3: Broadcast
-
-
Request via support ticket
Critical Reminder: Network addressing cannot be modified after creation.
Option 6: Virtual Router Overlay
Topology:
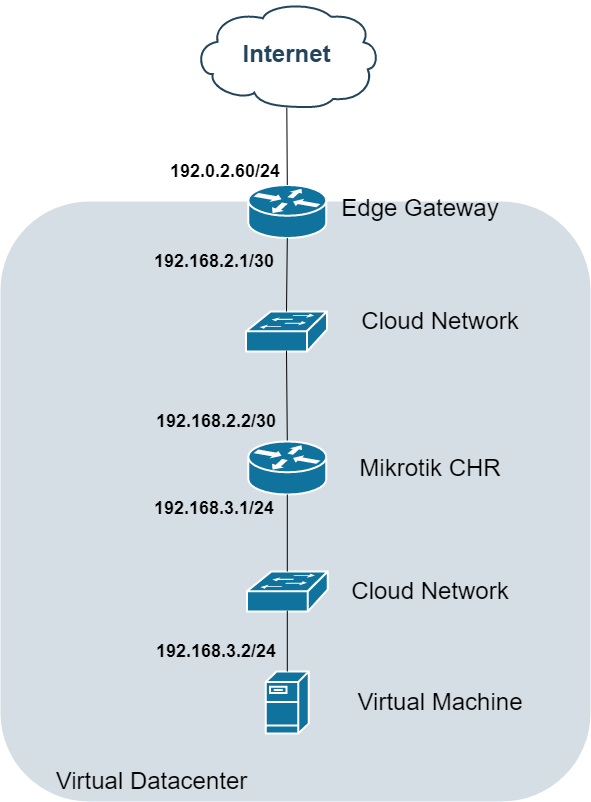
Considerations:
-
Deploy third-party routers (Cisco/Juniper/Mikrotik)
-
NAT still handled at Edge level
-
Maintains private addressing internally
Planning Recommendations
-
Address Space: Allocate 25% more IPs than currently needed
-
Growth: Prefer larger subnets for future expansion
-
Migration: Create new networks during maintenance windows
-
Documentation: Maintain IPAM records for all allocations
