The Container Service Extension (CSE) is an extension to VMware Cloud Director (VCD) that helps cloud tenants create and manage Kubernetes clusters.
CSE represents Kubernetes as a service in VCD, allowing providers the following:
- Create custom VM templates (Kubernetes templates)
- Import off-the-shelf VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid OVAs (TKG templates)
Users can deploy fully functional Kubernetes clusters as standalone vApps..
How CSE works
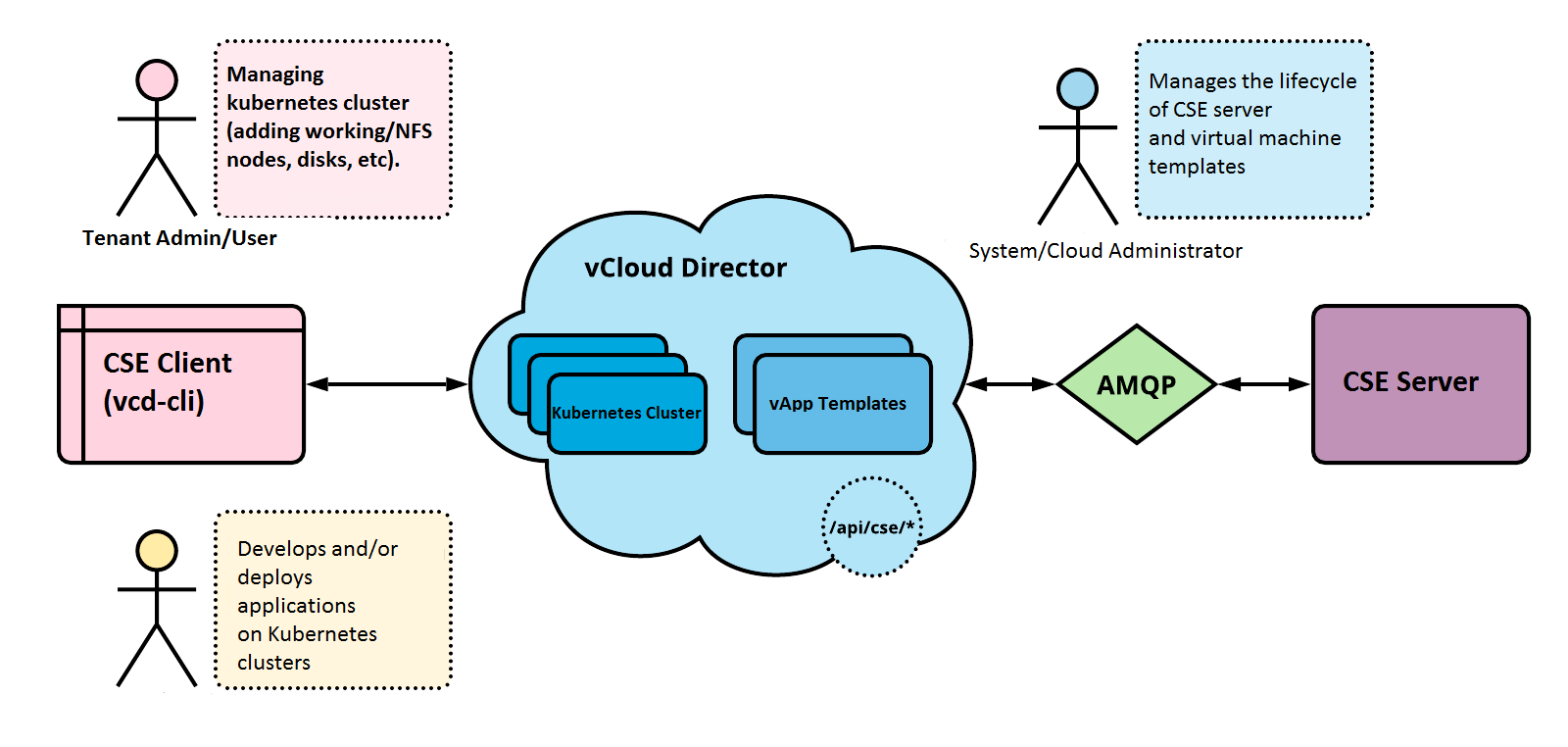
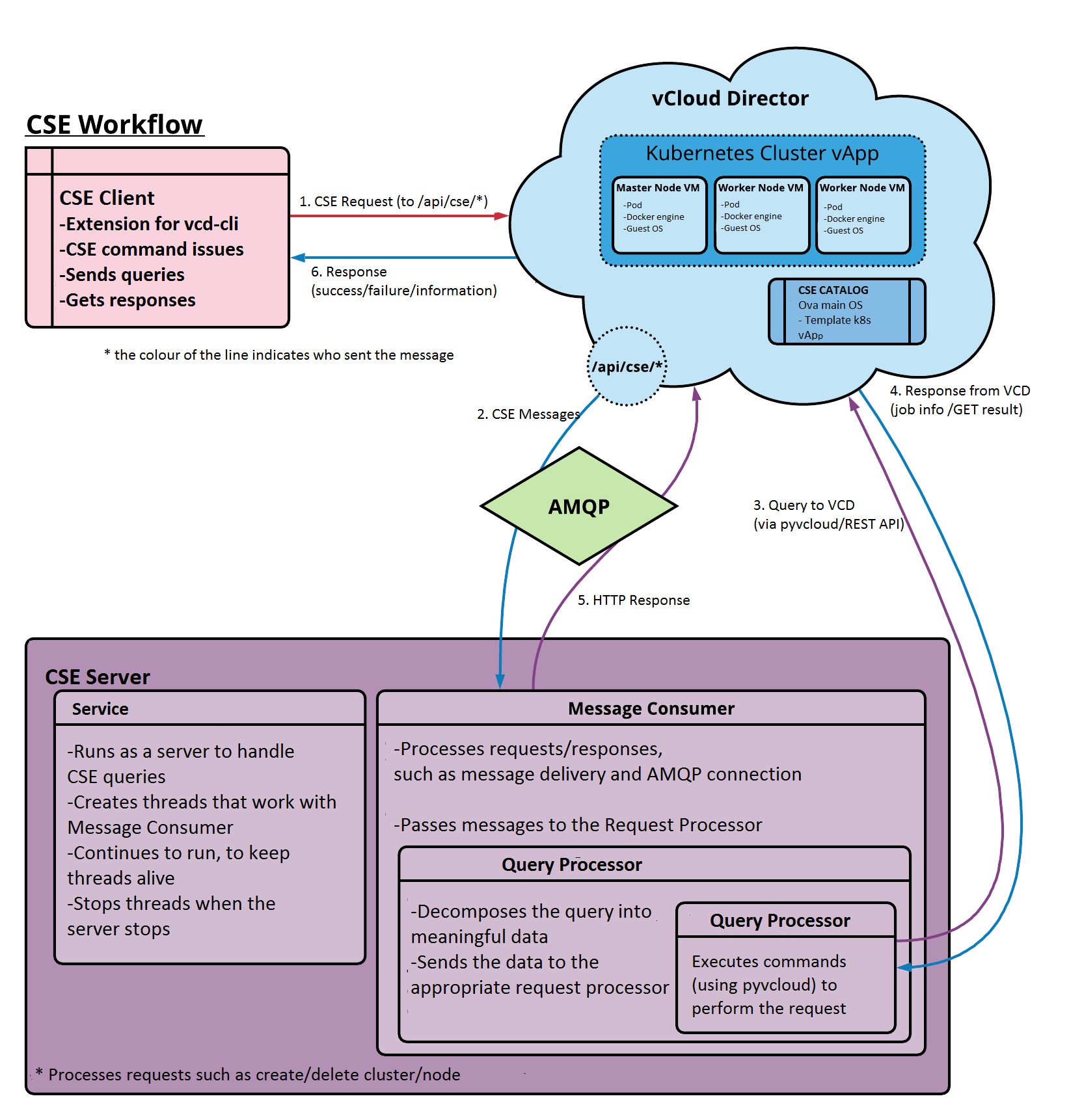
CSE consists of a server and a client component. The server component is installed as an extension to the VCD API. It provides REST API endpoints via VCD. The CSE client component connects to the vcd-cli, communicates with the CSE server via open API endpoints, and helps VCD users create Kubernetes clusters in VCD. The following diagram illustrates the interaction between the components.
Types of CSE users
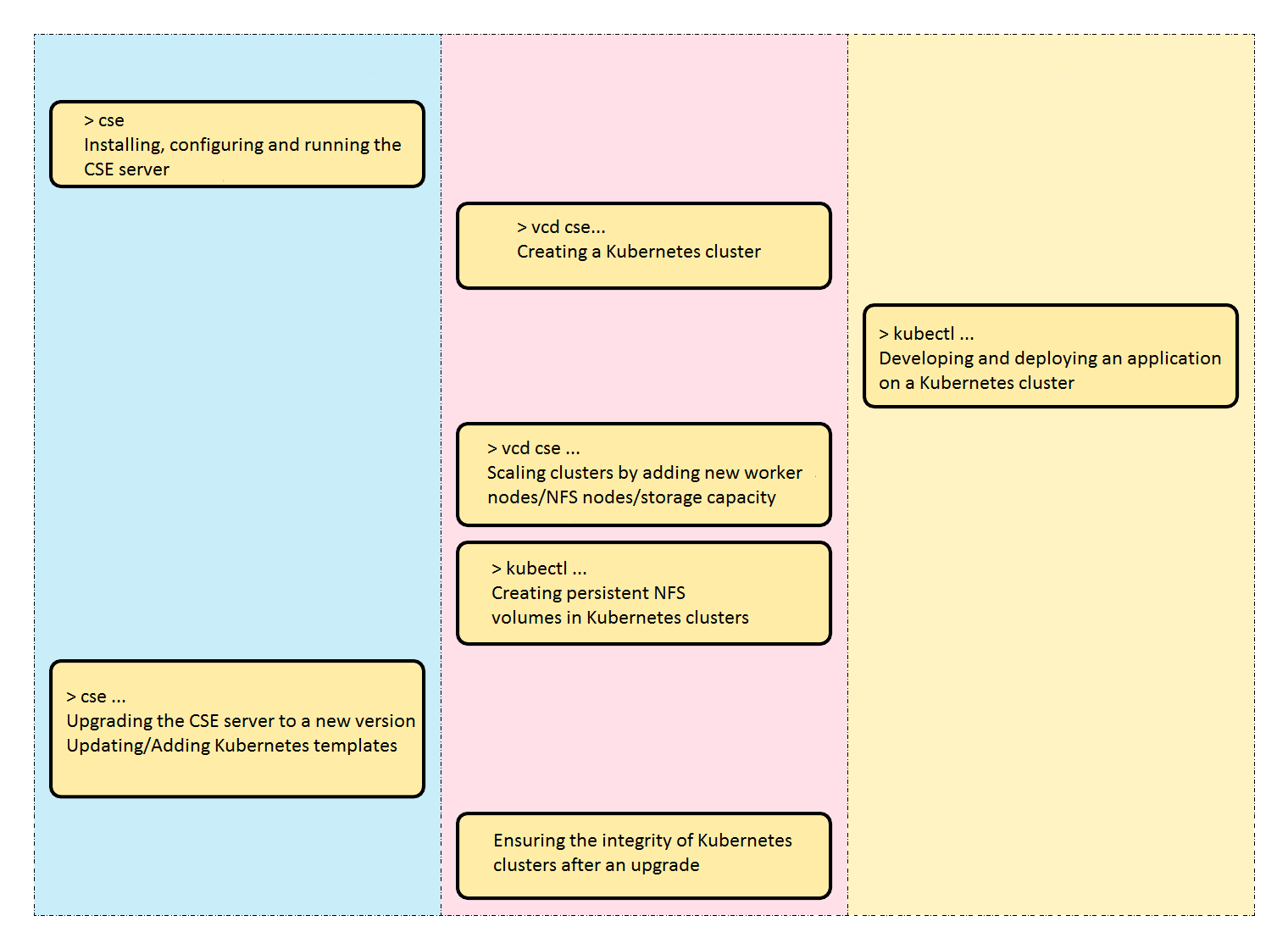
Cloud administrators. Responsible for configuring the VCD, CSE configuration file, CSE server and Kubernetes templates. Prior to CSE 3.0.0, the only VCD role required for cloud administrators was System Administrator. However, in CSE 3.0.1 and later versions, CSE provides the ability to create a CSE Service Role. Cloud administrators are expected to have this role and have VCD administration experience.
Note: If the CSE Service Role (for example, in VCD 10.1), cloud administrators can be assigned the System Administrator VCD.
Once the CSE server is running and Kubernetes templates are available, administrators and users of tenant organizations can use the CSE client (vcd-cli) to manage the Kubernetes cluster. This includes deploying clusters, adding worker nodes, configuring NFS storage, etc.
Tenant users who manage Kubernetes clusters must understand the principles of VCD org administration. They must have accounts with the necessary permissions to create and manage vApps. In addition, these users must understand Kubernetes cluster management, including configuring user access and defining persistent volumes.
Developers and other Kubernetes users interact with CSE Kubernetes clusters via kubectl. For these users, Kubernetes clusters work like any other Kubernetes cluster implementation. No special knowledge of VCD or CSE administration is required. These users do not even need a VCD account.